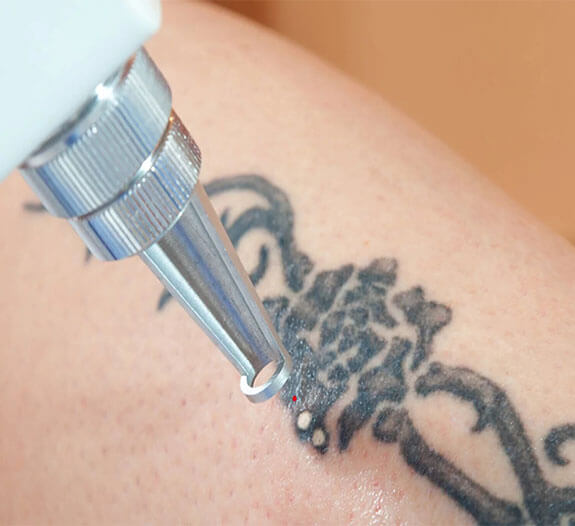
Methods of Tattoo Removal
Laser
Many physicians consider laser as one of the best methods of tattoo removal. Nowadays, the Q-switched Nd: Yag, Q-switched, Alexandrite and the Q-switched Ruby are among the most commonly used lasers for the removal of unwanted tattoos. A local anaesthetic cream to be applied prior to the treatment to numb the skin. The laser is directed onto the tattoo, breaking up the tattoo pigment and then over the next few weeks the body's scavenger cells remove that pigment from the treated areas. Usually, multiple sessions (8 to 10 sessions) are necessary to remove the entire tattoo at intervals of four weeks. Usually, multi-coloured tattoo removal almost always requires the use of two or more laser wavelengths.
Q-switched Nd: YAG 1064 nm
This laser is most suitable for darker skin. This laser wavelength is best absorbed by black colour tattoo pigments, hence, it is very effective to remove black coloured tattoos. It may be used in combination with other lasers for tattoos with red, green, yellow pigment.
Resurfacing
Resurfacing of tattoos can be done to remove only the top layers of the skin bearing the pigment. This technique usually not always removes the pigment of the tattoo present in the deeper layers of the skin. Resurfacing can be done through:
• Dermabrasion
• Ablative lasers like CO2 laser
Both the techniques may require local anaesthesia to numb the affected area because some bleeding is likely to occur and a dressing is applied immediately after the procedure to the treated area.
Regardless of which method of tattoo removal has been used, some variations in skin colour are possible to remain. Healing time varies depending upon the size and depth of the tattoo and the procedure used.
Side Effects of Tattoo Removal
Side effects are very less likely if it is treated by an experienced dermatologist but in some patients following side effects may occur:
- Hyperpigmentation (darkening) or hypopigmentation (whitening) may sometimes occur in treated areas, however, these are more common in darker skin. This can be avoided by doing a patch test, where the laser is applied to one test site prior to a decision to treat a full tattoo.
- Sometimes scarring may occur when inappropriate laser energy is used to treat.
- Transient textural changes may be noticed but often resolve within a few months
Contraindications for Tattoo Removal
- Patients with tendencies of hypertrophic scar or keloid
- Active inflammation or infection at the site of the tattoo.
- Patients with a history of Vitiligo, Psoriasis.
 Whatsapp
Whatsapp Facebook
Facebook Twitter
Twitter Instagram
Instagram Linkedin
Linkedin Pinterest
Pinterest