Different Types of Moles
Various studies have concluded that certain types of moles have a greater tendency of becoming cancerous. These moles may turn into a type of skin cancer that is known as malignant melanoma. Melanoma is associated with sun exposure and repeated sunburns increase the chances of melanoma.
1. Congenital nevi:
Some moles are present at birth in about 1 in 100 people. They are called congenital nevi. There is a greater chance of developing melanoma in such case when compared to the moles which appear later in life.
2. Dysplastic nevi or atypical moles:
These moles are larger than average (usually larger than a pencil eraser) and irregular in shape. They mostly have uneven color with dark brown centers and lighter, sometimes reddish, uneven border or black dots at edge. It is important for people with dysplastic nevi to visit a dermatologist regularly as they are more likely to develop malignant melanoma, hence regular check up to identify any changes is a must.
Precautions
-
Sudden growth.
-
Spontaneous bleeding.
-
Color change especially around the borders.
-
Sudden itching.
Other Pigmented Patches On The Skin
1. Freckles:
These are dark-colored spots on the skin that are not moles. Unlike moles, freckles are rarely larger than the size of a pea, although sometimes they may seem to be large because they blend into one another. Sun exposure is a major cause of the appearance and darkening of freckles. Therefore, freckles are mostly seen in the areas most exposed to the sun such as the face, neck, and upper back. In many cases, it is seen that during winter months freckles may fade completely.
2. Seborrheic keratoses:
After middle age, a person may acquire other dark areas that are not moles. These appear as brown, wart-like growths generally on the face or trunk and look as if they have been stuck onto the skin. These may be harmless growths.
3. Actinic lentigines:
Multiple small gray-brown spots that may appear on wrists, backs of the hands, forearms, and face could be actinic lentigines. These are often also referred to as 'liver spots’, ‘age spots’ or ‘sunspots’ although they are not associated with liver or age in any way. They are not cancers.
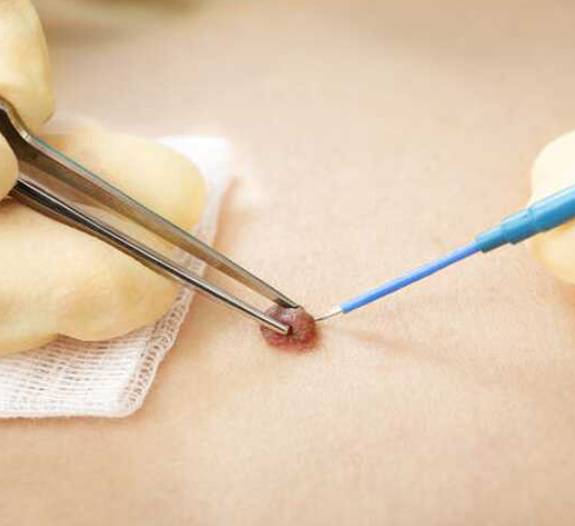
Treatment of Moles
The majority of moles and other blemishes are benign (not-cancerous). But certain moles act differently than other existing moles and that’s when medical intervention is needed. So, if any spot starts changing in terms of size, shape, color, or if it starts bleeding, itching, becoming painful or moles that appear when a person is past 20 yrs of age; they must immediately get in touch with a dermatologist.
If one notices a mole that does not follow the normal pattern, a dermatologist may be able to assure them that the mole is harmless, or confirm that it is cancerous. The dermatologist may remove the mole or part of it to study it under a microscope which is known as biopsy. If it is found that the mole is cancerous and only a part of it was removed for investigation then the doctor will suggest to remove the entire lesion and an extra margin as a safety measure.
If a person may wish to get rid of moles that are irritating them, or simply because they are unattractive. There are many methods that can be used to remove the mole such as numbing and shaving the mole off, or cutting out the entire lesion and stitching the area closed. These are quick procedures that can be performed in a dermatologist's office.
There are chances that a mole will recur after it is removed. So, if the mole starts to reappear after it has been removed, one must return to the dermatologist for investigation and treatment. Routine check up is advised yearly to monitor the moles. In case of a suspicious mole one must visit the dermatologist 6 monthly for a thorough check up.
 Whatsapp
Whatsapp Facebook
Facebook Twitter
Twitter Instagram
Instagram Linkedin
Linkedin Pinterest
Pinterest