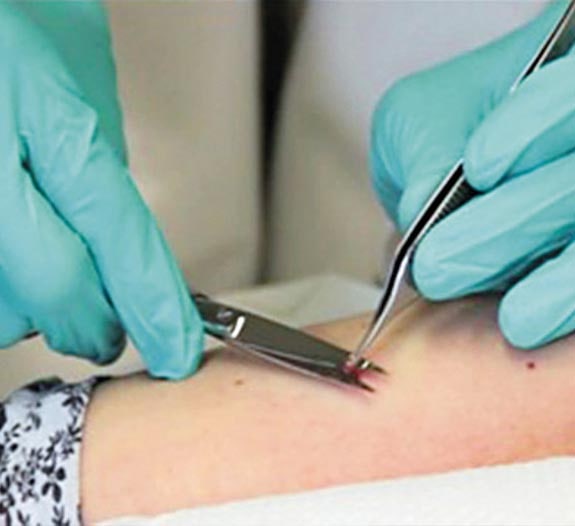
Procedure
Local anesthesia is used to numb the area being treated. The biopsy area will be cleaned. The skin is then sampled using one of the techniques of the above procedure. Shave biopsies mostly do not require stitches while punch, excisional, and incisional biopsies will usually be closed with sutures. The procedure usually takes 15 to 20 minutes. Once the procedure is complete, a clean dressing is placed to cover the area.
 Whatsapp
Whatsapp Facebook
Facebook Twitter
Twitter Instagram
Instagram Linkedin
Linkedin Pinterest
Pinterest