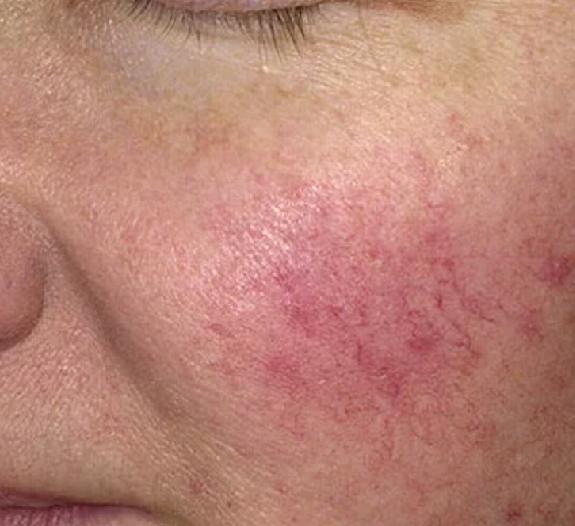
Triggering Factors
Sun exposure is a major triggering factor for rosacea, and other than that sudden temperature changes, hot showers, steam, and sauna can be held responsible for aggravating melasma. Dietary items such as alcohol especially red wine, caffeine, hot and spicy food and hot beverages such as tea and coffee are also can trigger this problem. Sometimes. Menopause, emotional stress and premenstrual hormonal fluctuations too can aggravate Rosacea.
Treatment
- The application of sunscreen daily with an SPF of 30+ is essential in the morning and afternoon.
- Light paraben-free, perfume-free moisturizers should be used to keep the skin calm.
- Sometimes antibiotics may be necessary; Metronidazole and Clindamycin gels are topical antibiotics that are used for mild cases. In severe cases, oral antibiotics can be used. Eg Doxycycline.
- Topical mild steroid creams rapidly reduce redness and swelling of the face in very severe cases for a very short period of time of about a week under a Dermatologist’s supervision. Steroid creams should not be used routinely on a long term basis as this can be very harmful to both rosacea as well as the skin and will eventually worsen the condition and the redness.
Maintenance Treatment
As Rosacea is a chronic condition with phases of clearance and flare-ups, so, understanding the triggers and avoiding them meticulously will go a long way to prevent flare-ups. Once the patient has achieved control over rosacea, one must understand that the skin continues to be prone to irritation and therefore patients have to avoid using beauty products and should continue to use their sunscreens and moisturizers regularly. A diary must be maintained to keep a record of when the flare-ups happen.
Treatment of sequelae
The skin bumps or pimples may get better quickly, but redness and flushing take longer to improve. Once a patient has achieved control over Rosacea then a dermatologist may consider light treatments such as IPL to reduce the redness and improve the texture of the skin. If the patient has developed a swollen, thickened and bumpy nose (termed as Rhinophyma) Ablative Radiofrequency or Surgical removal can be considered.
 Whatsapp
Whatsapp Facebook
Facebook Twitter
Twitter Instagram
Instagram Linkedin
Linkedin Pinterest
Pinterest