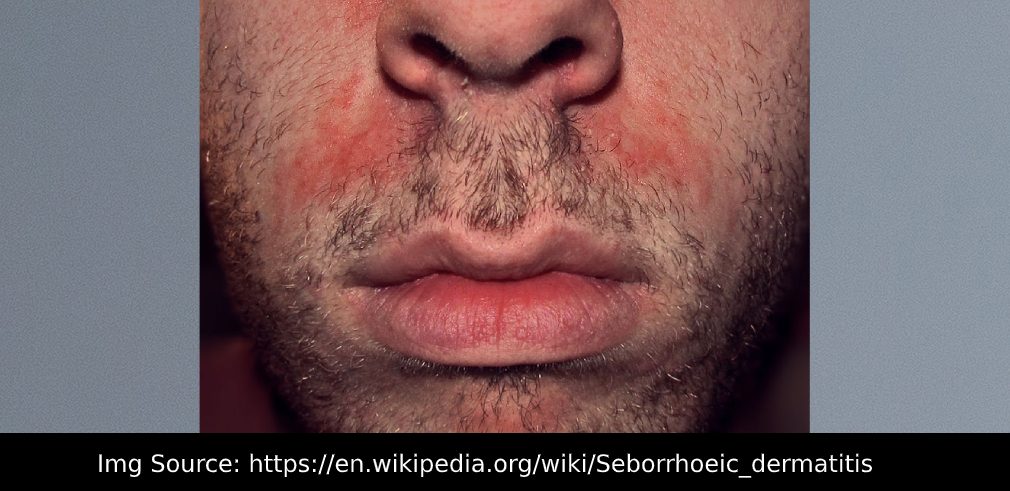
This is a common and relapsing skin condition affecting the sebaceous gland (oil secreting gland) rich areas of the body which are the scalp, face, central chest, ano- genital areas. It is characterized by erythematous or red patches with superficial yellowish greasy scales. It has a predilection for the skin folds. Over the face it is seen in the eyebrows, eyelashes, folds of the nose, beard area and behind the ears. Sometimes the scales from the eyelashes fall in the eyes resulting innredness of the eye and conjunctivitis. In dark skinned people, hypopigmented patches are a prominent feature. Involvement of the front of chest shows a typical petal shaped erythema and hence is called Patelloid variant.
If isolated to scalp it is called dandruff or pityriasis capitis. This can be considered the mildest form of seborrheic dermatitis. Itching is variable. It is extremely common and affects 1- 3 % of adult population. The cause is not fully understood but the most accepted mechanism is that the oil secretion increases under the influence of hormones in the young adults and the action of certain kind of fungus which lives on the skin inherently causes inflammation resulting in this condition.
This condition is more common in winter and improves with sun exposure and in summers. This condition typically has a chronic relapsing course.
This condition is also fairly common in the new borns where the mechanism is same due to the transfer of hormones from the mother to the child. In infants it presents as a thick yellow waxy crust on the scalp called the cradle cap or in the groin area.
This disappears spontaneously in an year’s time as the maternal hormone levels slowly reduce.
Rarely it can get complicated in adults with low immunity as in AIDS patients and can be extensive or become a life threatening condition called exfoliative dermatitis or erythroderma.
There is no definitive treatment for this condition but anti-inflammatory agents (steroids creams, tacrolimus and pimecrolimus) in combination with antifungals (clotrimazole, ketoconazole, sertaconazole, zinc pyrithione, selenium sulphide, etc) and medicines to reduce the scaling (salicylic acid, urea, lactic acid, coal tar) act fairly well in controlling the dermatitis. The most commonly encountered variant Dandruff is treated similarly with medications in various formulations like foams, creams and shampoos. Oral antifungal therapy is occasionally advocated for recalcitrant or widespread seborrheic dermatitis.
 Whatsapp
Whatsapp Facebook
Facebook Twitter
Twitter Instagram
Instagram Linkedin
Linkedin Pinterest
Pinterest